GITT (Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique) measurements of LixCoO2/Li half-cell voltages were numerically simulated based on Newman's well established electrochemical pseudo 2D model. The measurements revealed differences in the charge transfer kinetics between charging and discharging, which change with the state of charge of LixCoO2. To properly account for these differences in the simulations, SOC-dependent reaction-rate constant together with SOC-dependent charge transfer coefficients were introduced, which were unambiguously determined from the measured IR drops of the GITT pulses during charging and discharging. Furthermore, the SOC-dependence of the chemical Li-ion diffusion coefficient in LixCoO2 was analyzed by fitting the GITT data within the framework of the pseudo 2D model, as well as by means of classical analysis by Weppner and Huggins [W. Weppner and R. A. Huggins, J. Electrochem. Soc. 124 (1977) 1569]. Improvement of the simulation of GITT measurements using SOC-dependent rate constants and charge transfer coefficients compared to SOC-independent values is demonstrated.
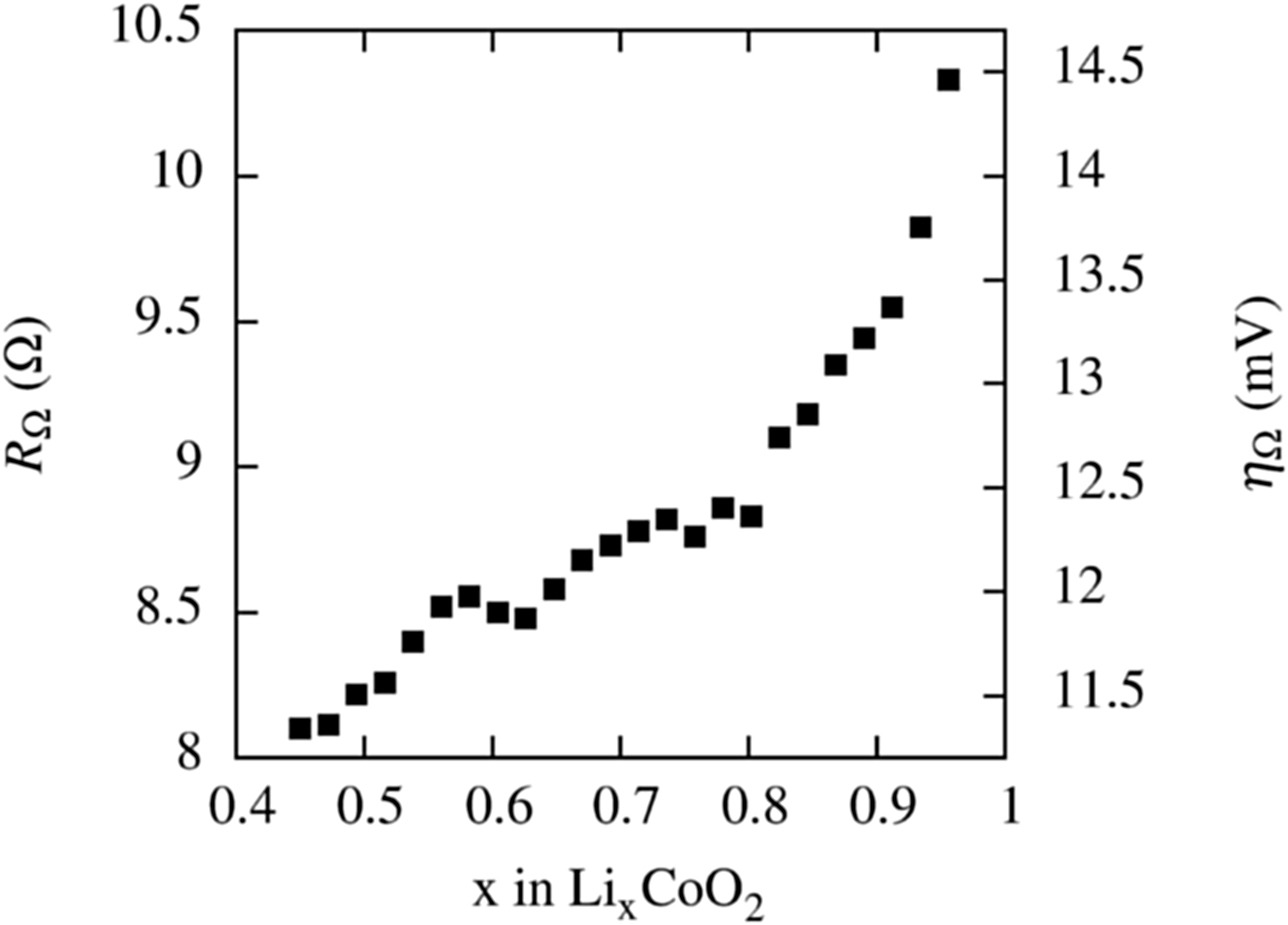
GITT (Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique) measurements of LixCoO2/Li half-cell voltages were numerically simulated based on Newman's well established electrochemical pseudo 2D model. The measurements revealed differences in the charge transfer kinetics between charging and discharging, which change with the state of charge of LixCoO2. To properly account for these differences in the simulations, SOC-dependent reaction-rate constant together with SOC-dependent charge transfer coefficients were introduced, which were unambiguously determined from the measured IR drops of the GITT pulses during charging and discharging. Furthermore, the SOC-dependence of the chemical Li-ion diffusion coefficient in LixCoO2 was analyzed by fitting the GITT data within the framework of the pseudo 2D model, as well as by means of classical analysis by Weppner and Huggins [W. Weppner and R. A. Huggins, J. Electrochem. Soc. 124 (1977) 1569]. Improvement of the simulation of GITT measurements using SOC-dependent rate constants and charge transfer coefficients compared to SOC-independent values is demonstrated.
