The electronic and photoconductive characteristics of CdTe nanowire-based field effect transistors were studied systematically. The electrical characterization of a single CdTe nanowire FET verifies p-type behavior. The CdTe NW FETs respond to visible-near infrared (400-800 nm) incident light with a fast, reversible and stable response characterized by a high responsivity (81 A W(-1)), photoconductive gain (2.5 - 10(4)%) and reasonable response and decay times (0.7 s and 1 s, respectively). These results substantiate the potential of CdTe nanowire-based photodetectors in optoelectronic applications.
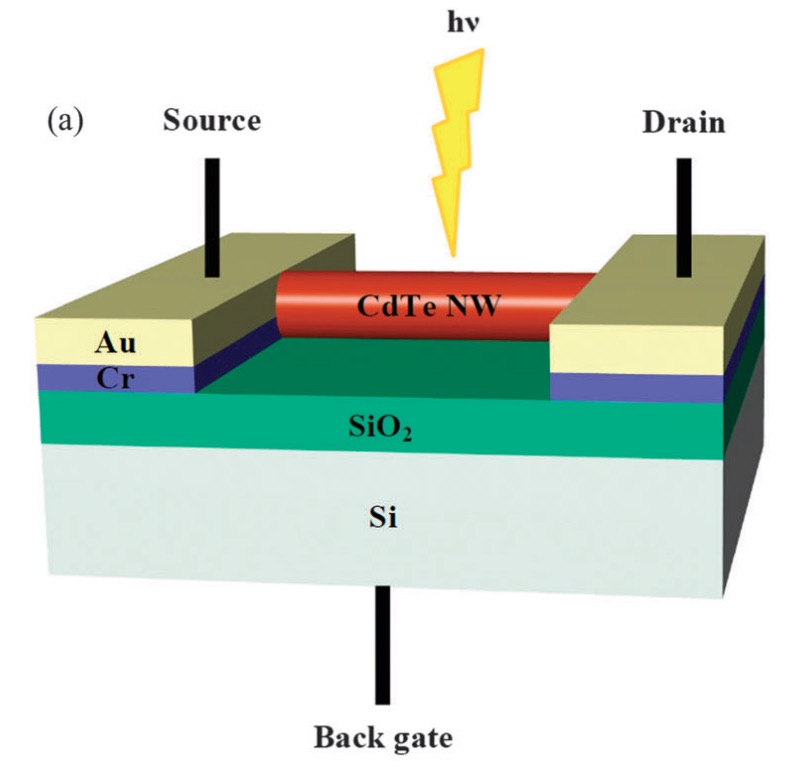
The electronic and photoconductive characteristics of CdTe nanowire-based field effect transistors were studied systematically. The electrical characterization of a single CdTe nanowire FET verifies p-type behavior. The CdTe NW FETs respond to visible-near infrared (400-800 nm) incident light with a fast, reversible and stable response characterized by a high responsivity (81 A W(-1)), photoconductive gain (2.5 - 10(4)%) and reasonable response and decay times (0.7 s and 1 s, respectively). These results substantiate the potential of CdTe nanowire-based photodetectors in optoelectronic applications.
