The molecular quantum cellular automata paradigm (m-QCA) offers a promising alternative framework to current CMOS implementations. A crucial aspect for implementing this technology concerns the construction of a device which effectively controls intramolecular charge-transfer processes. Tentative experimental implementations have been developed in which a voltage drop is created generating the forces that drive a molecule into a logic state. However, important factors such as the electric field profile, its possible time-dependency and the influence of temperature in the overall success of charge-transfer are relevant issues to be considered in the design of a reliable device. In this work, we theoretically study the role played by these processes in the overall intramolecular charge-transfer process. We have used a Landau-Zener (LZ) model, where different time-dependent electric field profiles have been simulated. The results have been further corroborated employing density functional tight-binding method. The role played by the nuclear motions in the electron-transfer process has been investigated beyond the Born-Oppenheimer approximation by computing the effect of the external electric field in the behavior of the potential energy surface. Hence, we demonstrate that the intramolecular charge-transfer process is a direct consequence of the coherent LZ nonadiabatic tunneling and the hybridization of the diabatic vibronic states which effectively reduces the trapping of the itinerant electron at the donor group.
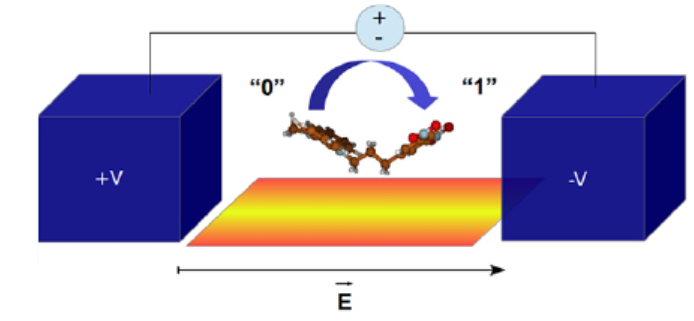
The molecular quantum cellular automata paradigm (m-QCA) offers a promising alternative framework to current CMOS implementations. A crucial aspect for implementing this technology concerns the construction of a device which effectively controls intramolecular charge-transfer processes. Tentative experimental implementations have been developed in which a voltage drop is created generating the forces that drive a molecule into a logic state. However, important factors such as the electric field profile, its possible time-dependency and the influence of temperature in the overall success of charge-transfer are relevant issues to be considered in the design of a reliable device. In this work, we theoretically study the role played by these processes in the overall intramolecular charge-transfer process. We have used a Landau-Zener (LZ) model, where different time-dependent electric field profiles have been simulated. The results have been further corroborated employing density functional tight-binding method. The role played by the nuclear motions in the electron-transfer process has been investigated beyond the Born-Oppenheimer approximation by computing the effect of the external electric field in the behavior of the potential energy surface. Hence, we demonstrate that the intramolecular charge-transfer process is a direct consequence of the coherent LZ nonadiabatic tunneling and the hybridization of the diabatic vibronic states which effectively reduces the trapping of the itinerant electron at the donor group.
