The oral cavity is an easily accessible unique environment and open system which is influenced by the oral fluids, microbiota, and nutrition. Little is known about the kinetics and dynamics of metabolic processes at the intraoral surfaces. Real-time monitoring of salivary biomarkers, e.g., glucose, lactate, fluoride, calcium, phosphate, and pH with intraoral sensors is therefore of major interest. The aim of this review is to overview the existing literature for intraoral saliva sensors.
A comprehensive literature search was performed to review the most relevant studies on intraoral saliva sensor technology.
There is limited literature about the in situ saliva monitoring of salivary biomarkers. Bioadhesion and biofouling processes at the intraoral surfaces limit the performances of the sensors. Real-time, long-term, and continuous intraoral measurement of salivary metabolites remains challenging and needs further investigation as only few well-functioning sensors have been developed until today. Until now, there is no sensor that measures reliably beyond hours for any analyte other than glucose
Saliva’s complex and dynamic structure as well as bioadhesion are key challenges and should be addressed in the future developments. Consequently, more studies that focus particularly on biofouling processes and interferential effects of the salivary matrix components on sensor surfaces are required.
By monitoring fluids in the oral cavity, as the entrance to the digestive system, extensive information can be obtained regarding the effects of foods and preventive agents on the oral microbiota and the tooth surfaces. This may lead to a better understanding of strategies to modulate oral and general health.
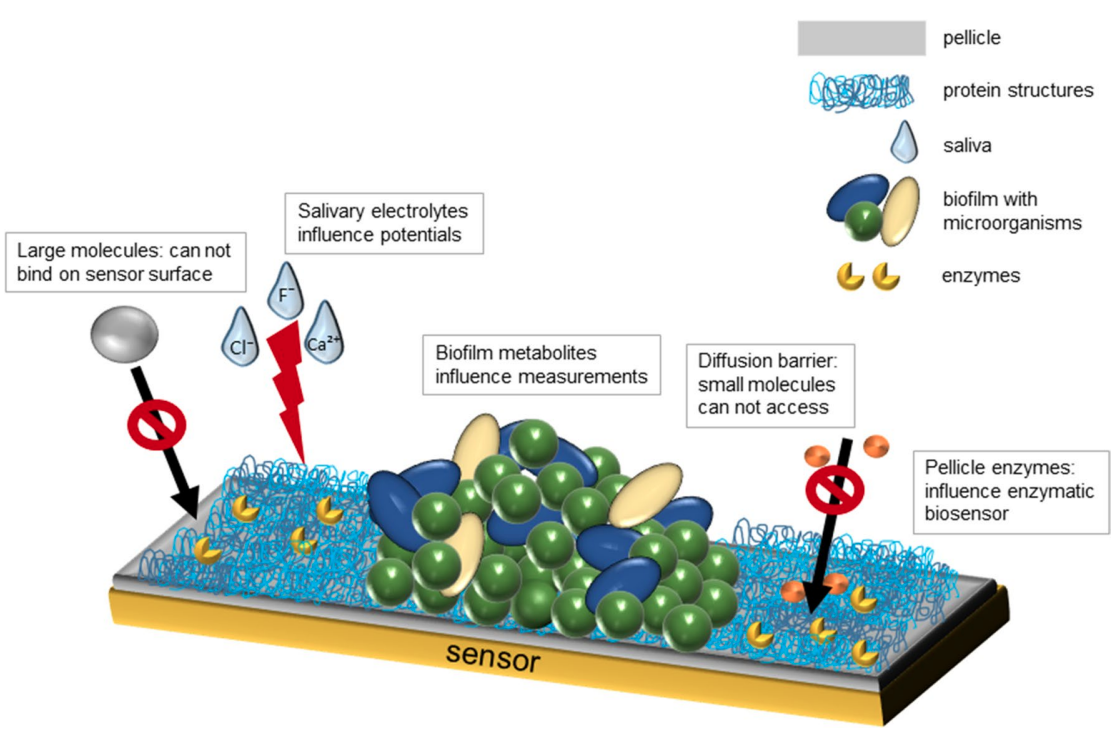
The oral cavity is an easily accessible unique environment and open system which is influenced by the oral fluids, microbiota, and nutrition. Little is known about the kinetics and dynamics of metabolic processes at the intraoral surfaces. Real-time monitoring of salivary biomarkers, e.g., glucose, lactate, fluoride, calcium, phosphate, and pH with intraoral sensors is therefore of major interest. The aim of this review is to overview the existing literature for intraoral saliva sensors.
A comprehensive literature search was performed to review the most relevant studies on intraoral saliva sensor technology.
There is limited literature about the in situ saliva monitoring of salivary biomarkers. Bioadhesion and biofouling processes at the intraoral surfaces limit the performances of the sensors. Real-time, long-term, and continuous intraoral measurement of salivary metabolites remains challenging and needs further investigation as only few well-functioning sensors have been developed until today. Until now, there is no sensor that measures reliably beyond hours for any analyte other than glucose
Saliva’s complex and dynamic structure as well as bioadhesion are key challenges and should be addressed in the future developments. Consequently, more studies that focus particularly on biofouling processes and interferential effects of the salivary matrix components on sensor surfaces are required.
By monitoring fluids in the oral cavity, as the entrance to the digestive system, extensive information can be obtained regarding the effects of foods and preventive agents on the oral microbiota and the tooth surfaces. This may lead to a better understanding of strategies to modulate oral and general health.
